What Causes the Microvascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus?
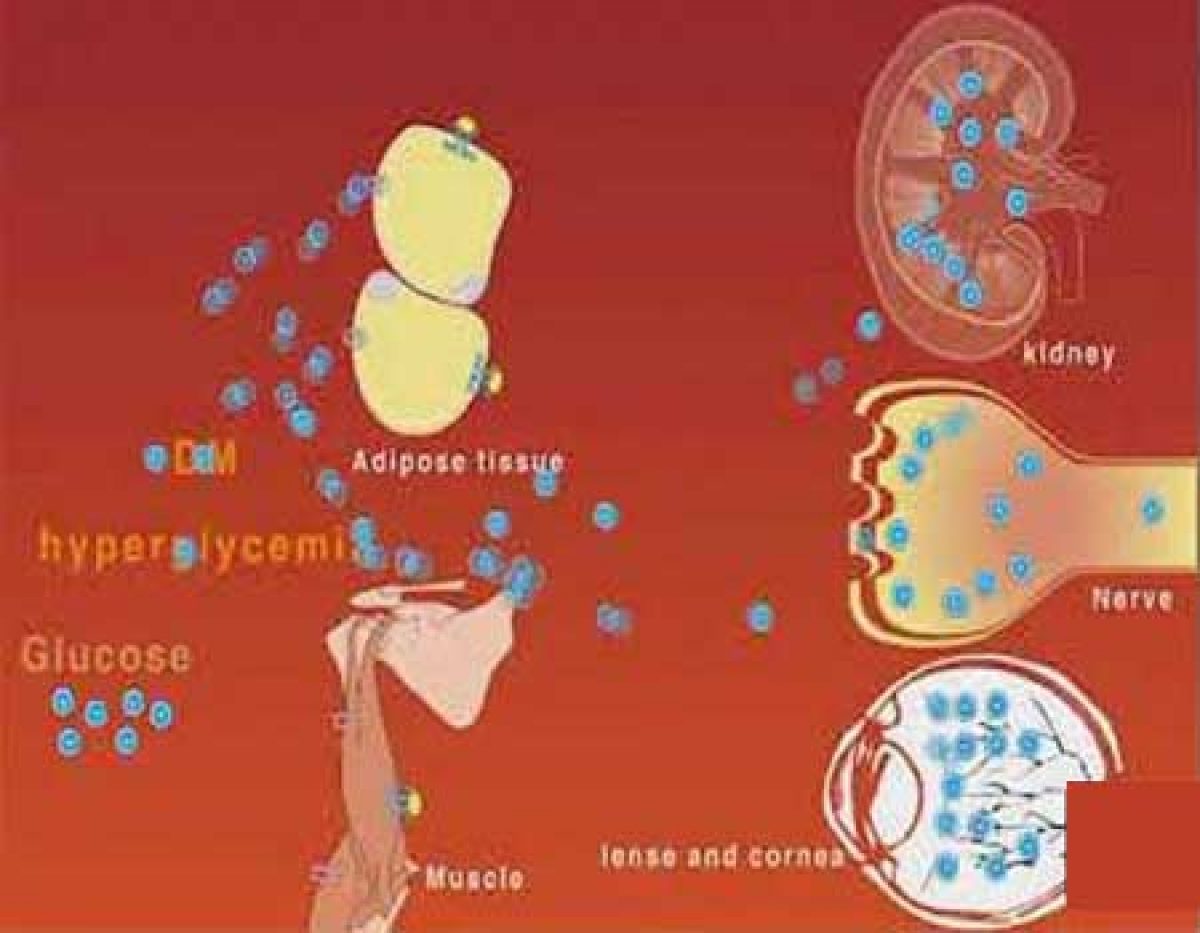
What Causes the Microvascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus? : Over time, diabetes has proven to be a serious health problem all over the world. Its association with vascular complications is what adds salt to the insult. Microvascular complications of diabetes refer to those chronic complications that have an impact on small blood vessels. The most common examples of micro-vascular complications include:
- Retinopathy
- Nephropathy
- Neuropathy
A good number of patients with diabetes will have either one or more of the above complications. The leading contribution to these complications in diabetic patients is due to the rise in the flux of sugar molecules via the polyol pathway.
The cause of this increase is the presence of high glucose levels. In turn, the increase in flux sugar leads to sorbitol accumulation in cells. The resulting osmotic stress due to sorbitol accumulation has proven beyond doubt to be the fundamental mechanism in the growth of microvascular complications.
Read the full content of What Causes the Microvascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus?
Table of Contents
Diabetic retinopathy
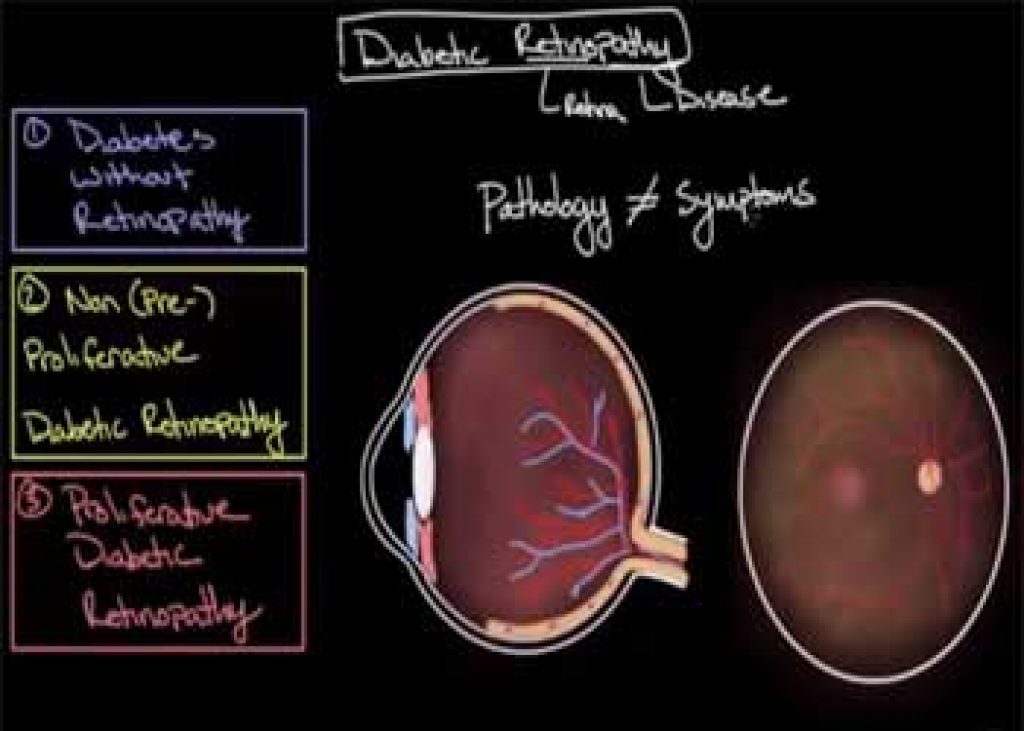
This is widely recognized as the most common form of microvascular complication associated with diabetes. Its main cause is having high sugar content in your blood which may damage your retina. The retina is a part of the eye that detects light and transmits signals to your brain via a nerve located at the back of your eye referred to as the optic nerve.
In the United States alone, it leads to over 10000 cases of blindness annually. It is hence the most common agent of visual loss to individuals within the working-age brackets across the globe. The risk of one developing diabetic retinopathy is dependent on both duration and the severity of hyper-glycemia. Its occurrence can be attributed to hyperglycemia-mediated damage which happens within the retinal microvasculature.
The results of this damage include:
- Thickening of the basement membrane
- Increased capillary permeability
- Formation of micro-aneurysms
The occurrence of the above-listed defamations leads to intravascular coagulation which in turn results in retinal ischemia. Retinal ischemia leads to the formation of new blood vessels within the retina which is delicate and their rupture leads to retinal bleeding. Besides, the deficiency of lymphatic drainage inside the retina leads to fluid accumulation in the presence of hyperglycemia resulting in muscular edema.
The greatest risk contributors to the development and maturity of retinopathy are; diabetes duration, glycemic control, and blood pressure. Evidence proves that steady improvement in glycemic control will lead to a transient worsening of retinopathy. Retinopathy tends to decrease during pregnancy. It is therefore advisable for pregnant ladies to visit health facilities for retinal assessment soon after their first appointment and in the 28th week of the pregnancy.
Management
Visual loss as a result of diabetic retinopathy can be prevented as well as cured and treated. Advanced medical management will greatly reduce the occurrence and progression of retinopathy. Identification during its initial stages allows for timely treatment aided by the use of laser photocoagulation and thus reduces the incidence of visual loss.
Risks associated with visual loss due to diabetic retinopathy are reduced through the following categories: primary prevention of microvascular complications, early detection of retinopathy, and finally effective treatment of established disease. Primary prevention is made possible through the control of optimum glycemic control.
The control of blood pressure levels also plays an important role in ensuring that diabetic retinopathy is managed as well as prevented. The application of lipid-lowering agents also reduces serum cholesterol levels that are associated with an increased risk of visual loss in patients with diabetic retinopathy.
For individuals with diabetes, it is always wise to get regular eye exams. This is because if discovered at its initial stages, diabetic retinopathy can be treated and thus impede blindness.
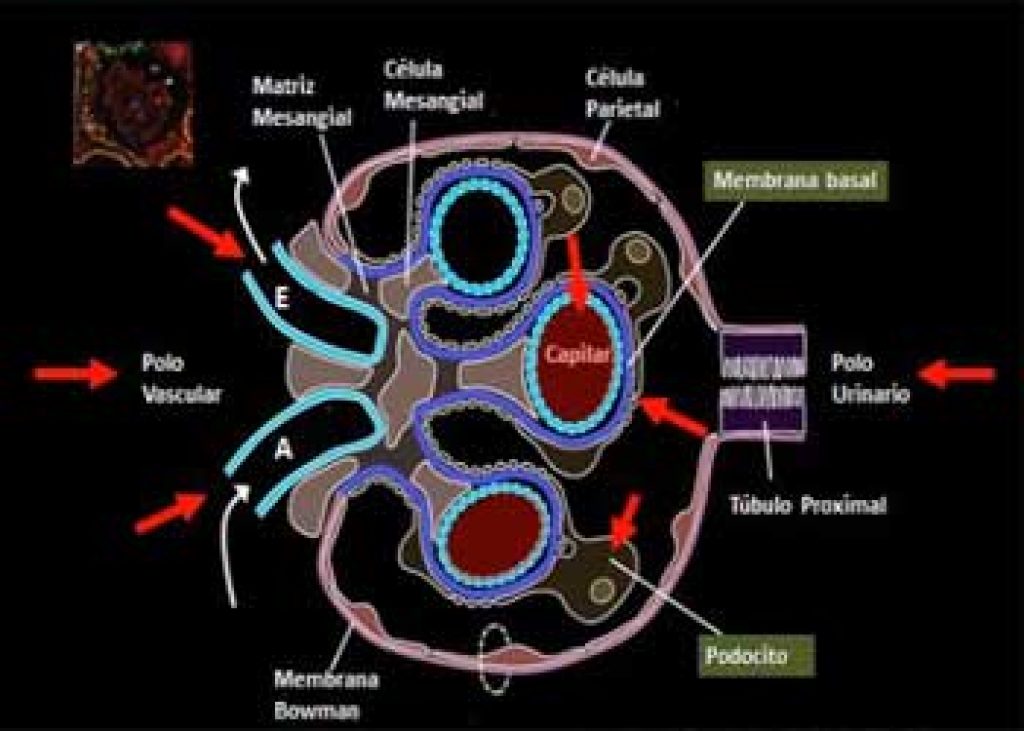
Diabetic nephropathy
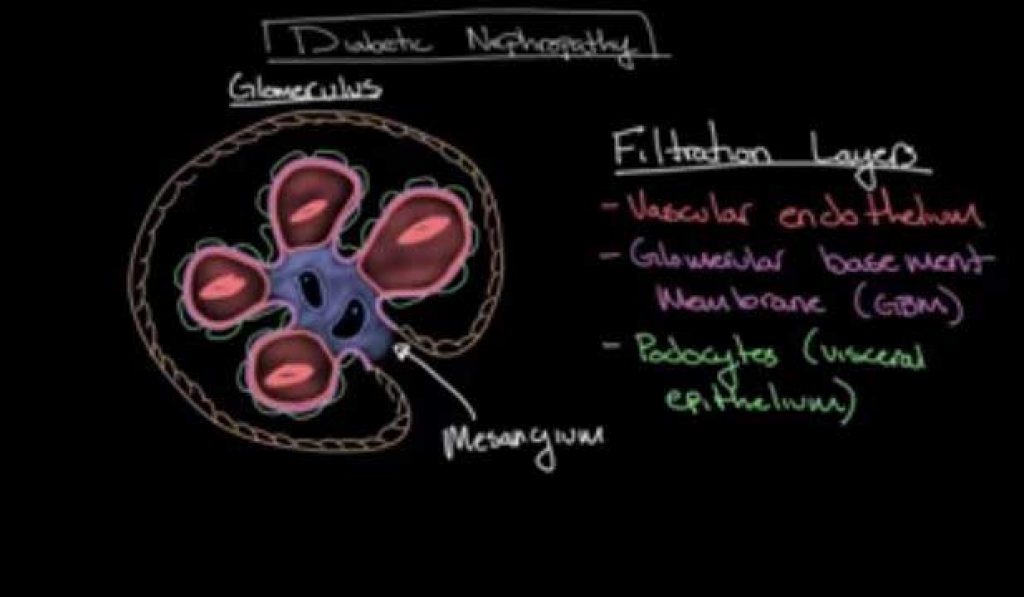
This is a sort of progressive kidney disease that in most situations affects individuals with diabetes, that is, type 1 and 2 diabetes. The extent of risk increases depending on the duration the disease has lasted.
Recent research shows that this type of diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure in the United States. Physicians therefore ought to have a deeper understanding of how diabetes and vascular diseases are related to curbing the gradual increase and prevalence of such complications.
This form of the disorder is brought about by the cooperation of hyperglycemia and hypertension leading to glomerular destruction. The basic pathological changes constitute thickening of the basement membrane, atrophy, interstitial fibrosis as well as arteriosclerosis.
During the initial stages, there is glomerular hyper-filtration in the kidney but as time goes on, progressive loss of the normal renal function takes place. Statistics show that diabetic nephropathy affects about 30- 40% of patients within the age bracket of 25 years.
Micro-albuminuria
A continued rise in glomerular filtration pressures contributes to albuminuria, which steers more damage to the already existing renal damage. Without timely intervention, patients diagnosed with diabetes and have micro-albuminuria always progress to proteinuria and reveal diabetic nephropathy. This progression manifests itself in both type 1 and 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, patients with type 2 diabetes may already possess micro-albuminuria before they are even diagnosed with diabetes.
A study conducted by the European Diabetes Prospective Complications indicates that the total occurrence of micro-albuminuria in patients with type 1 diabetes is approximately 12% within 7 years. According to a UKPDS study, the occurrence of micro-albuminuria was projected to be 2% annually in patients with type 2 diabetes. Its 10-year prevalence upon diagnosis was indicated to be 25%.
The following are some of the pathological changes that take place in the kidney due to diabetic nephropathy:
- Increased thickness in the glomerular membrane of the kidney
- Formation of micro-aneurysm
- Formation of mesangial nodule, that is, Kimmelsteil-Wilson bodies
The requirements for screening for diabetic nephropathy include a 24- hour urine collection or even a spot on urine measurement of micro-albumin. However, incidences of falsely elevated urine protein levels may arise due to conditions such as urinary tract infections, exercise, and hematuria.
Some of the factors that have been shown to lead to increases in diabetes nephropathy include:
- Having an origin of an African-American, Hispanic, or American Indian
- Your family has a history of kidney disease
- Been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes while you are aged 20 or below
- Smoking
The kidney can also be damaged by persistent high blood sugar as well as high blood pressure levels. Upon destruction, the kidneys will cease functioning normally and will therefore be unable to filter waste and get rid of excess water from the body.
Management
Prevention is always better than cure. While managing diabetes nephropathy, the initial and assured treatment is prevention. Just like any other microvascular complications of diabetes, there will always be a powerful association between glucose control and the risk of contracting diabetic nephropathy.
Therefore, patients ought to be treated to the least glucose level which is safe and just able to prevent or even control and curb diabetic nephropathy. Though treatment using angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) does not prove as an assured way of controlling the growth of micro-albuminuria in patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, it does reduce the risk associated with the development of diabetic nephropathy to patients who are type 2 diabetic.
To complement the aggressive treatment of high glucose levels, diabetic nephropathy patients may as well benefit from treatment with anti-hypersensitive drugs. Besides, the renin-angiotensin system blockade conveys extra benefits past the simple blood lowering mandate.
Also, ACE inhibitors and anti-otensin receptor blockers (ARBs) tend to reduce the risk associated with progression to microalbuminuria by about 60-70%. The use of these drugs has also been shown to reduce the risk of progression of kidney disease. It also leads to additional Renoprotective effects.
However, it is important to note that patients administered with these drugs may experience an early increase in creatinine, and monitoring of hyperkalemia is thus needed.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Based on the American Diabetes Association, (ADA), neuropathy is termed as the presence of symptoms or signs of peripheral nerve dysfunction in patients diagnosed with diabetes upon the exclusion of any other contributing factors.
Just like the rest of the micro-vascular complications discussed above, the chances of contracting neuropathy are dependent upon both the magnitude and duration of hyperglycemia. High blood sugar levels sustained over a long period are the main cause of Diabetic Neuropathy. Additional factors capable of causing nerve damage include:
- Destruction of blood vessels as a result of high cholesterol levels
- Mechanical injury, such as injuries sustained due to carpal tunnel syndrome
- Lifestyle factors which may comprise smoking or alcohol use
Declined levels of vitamin B-12 is also a probable cause of neuropathy
Management
Glycemic control has the potential to reduce its progression. However, this can only be accomplished at the early stages. This is because once the neuropathy has been established; glycemic control has minimal effect in controlling pain which happens to be the main symptom.
Patients diagnosed with this complication have to be informed on the importance of maintaining proper foot care and putting on appropriate footwear since they are exposed to higher chances of developing ulcers. Patients should also have easy access to podiatry and chiropody services for regular assessment of their feet.
Prevention of microvascular complications

In addition to visual, renal, and neurologic loss, these complications can negatively impact an individual’s lifestyle. This is because they may impair one’s mobility and cognition thus leading to poor quality of life. They may also limit the range of employment opportunities available to diabetic individuals which will immensely affect their productivity.
The patient may also incur unplanned expenses while seeking medical care and treatment thus encountering an extra economic burden. Sometimes, these complications eventually lead to the death of the patient.
This review, therefore, focuses on the possible prevention measures one can take to complement the tight glycemic therapy. Identification of the risk factors will play a vital role in equipping you with the necessary knowledge on how to prevent the complications. Some of the risk factors include:
- Uncontrolled use of tobacco
- Unhealthy cholesterol levels
- High blood pressure
- Intake of an unhealthy diet
- Living of a sedentary lifestyle whereby you are inactive in most hours of the day
- Diabetes
- Deficiency of estrogen especially in women
- Old age (usually more than 45 years for men and 55 years in women)
- Long term inflammation
The following are some of the key practices you can do to help prevent the complications if you are yet to witness them. These practices can also help sustain the complications without having to seek medical care all the time.
You should quit smoking or any form of tobacco use. Tobacco products may affect the kidney and in turn, add an extra burden to them thus making it extremely difficult to multi-task. In case you have problems quitting, you can always seek help from your doctor or rehabilitation centers.
Intake of a healthy diet is also recommended. This diet may comprise whole grains, lean meat, low-fat dairy, fruits, and vegetables. While preparing your diet, you should ensure that you limit salt, sugar, and alcohol. You should also get rid of saturated fats and Trans fats. Diabetic patients are always made aware of the best foods and drinks to take and the ones to avoid by their doctors.
Upon confirmation of diabetes, you should always try to control your blood sugar levels to help reduce the impacts of the complications. It is always a good practice to work hand in hand with your doctor to put up blood sugar goals that are right for you.
Always conduct regular checks on your blood cholesterol levels. If you find out that your cholesterol, levels are high; it is advisable to change your medication and diet to lower the number. This in turn protects your cardiovascular health.
Maintenance of a healthy weight is also vital. Excess weight tends to overwork your heart and contributes to high cholesterol levels, hypertension, and diabetes.
You May Like Also:
Top 10 Best Yeast Infection Treatments over the Counter
Top 6 Best Heat Pads for The Neck for Women- Reviews and Comparison
Top 6 Best Shiatsu Foot Massager Machine with Heat: Reviews and Guide
Final Thought
On the basis of several studies, tight glycemic control coupled with aggressive blood pressure control and maintenance of the required cholesterol levels will help minimize the progression of both nephropathy and retinopathy.
Diabetic patients assisted by their health professionals should always remain vigilant to detect the above micro-vascular complications at the initial stages. This helps avoid encountering potentially devastating complications due to realization at advanced levels.






